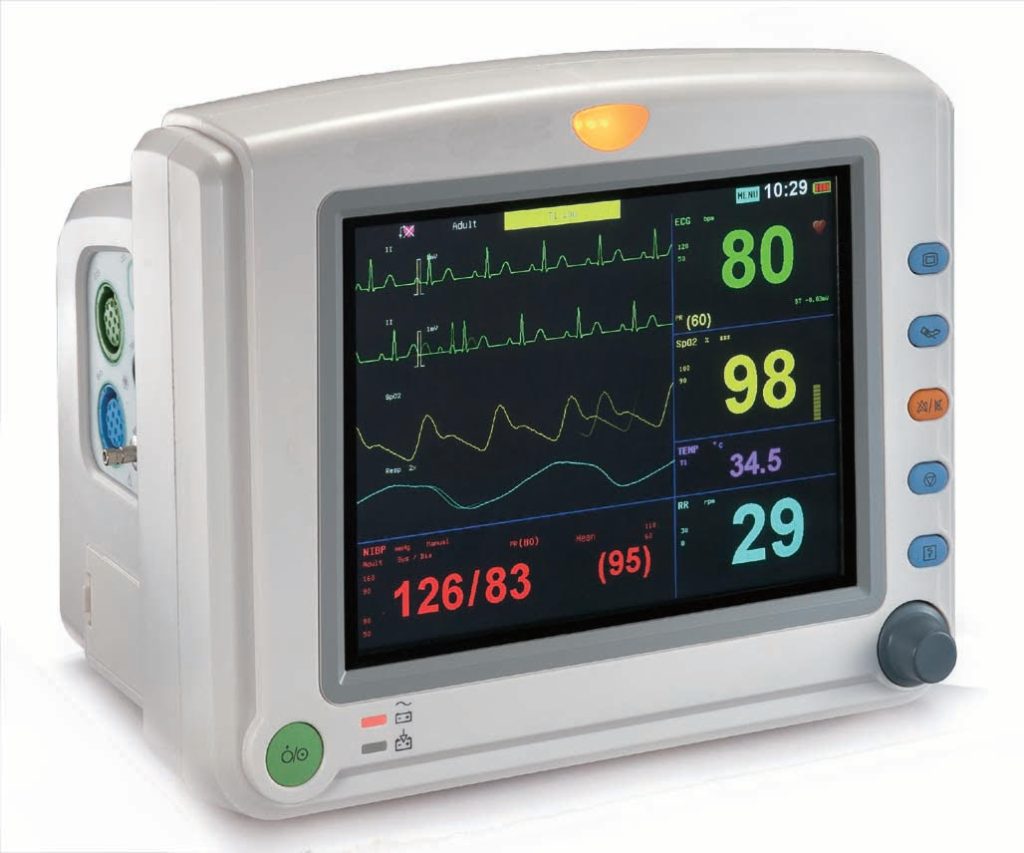
Among these devices, we have the darling of doctors and nurses, the Multiparameter Monitor like in Karl Storz Monitors for instance, which usually has a black background and colored parameters for easy viewing. As the name implies, the main objective of this equipment is to present to the doctor, in real-time, the patient’s condition, whether he is stable or not.
In addition, it continuously checks the heartbeat, allowing the doctor to act in advance, preventing deaths. The patient monitor can be configured in different parameters. We’ll talk about the main ones: ECG, Spo2, PI, PNI, FR, and Temp.
ECG – Electrocardiogram
The electrocardiogram parameter, or simply ECG, is a graphical representation of the heart’s electrical activity during its functioning. It is possible to calculate the heart rate, that is, the speed of the cardiac cycle, which will be measured by the number of heart contractions per minute (bpm).
With the electrodes on the patient’s body, signals will be generated, which are called leads; these are captured by an ECG cable, which can be 3 or 5 ways.
Depending on the type of pathology, the leads have different changes, which allows the physician to make an assertive diagnosis.
Spo2 – Oximetry
Spo2, or pulse oximetry, means peripheral capillary oxygen saturation, which estimates the amount of oxygen in the blood, in other words, the percentage of oxygenated hemoglobin. Normal values for Spo2 are between 95 and 100%, which will determine the efficiency of the patient’s respiratory system. They are captured by an oximetry sensor and have two methods to measure, spectrometry and photoplethysmography.
PI – Invasive Pressure
For this parameter to be monitored, the help of equipment/accessories will be necessary to perform the measurement well. It will be measured by conducting hydrostatic pressure to an electromechanical device, also known as a pressure transducer, which will transform the more complicated energy to measure directly into an easier type, such as electrical.
Pni – Non-Invasive Pressure
Unlike PI, for the PNI parameter to be measured, it is unnecessary to invade the patient’s body. This pressure results from the heartbeat and the resistance that blood flow undergoes through the vessel wall. There are two types of pressure, systolic and diastolic. Normal values for systolic blood pressure are 90 to 130 mmHg, and diastolic blood pressure is 60 to 90 mmHg. To obtain measurements of this parameter, a cuff or cuff is used.
Fr – Respiratory Rate
The respiratory rate is calculated through the respiration parameter registered by the ECG electrodes, which identifies peaks in respiration to detect possible events. Normal values for an adult range from 12 to 18 times per minute, 25 to 30 breaths per minute in children, and 30 to 40 breaths per minute in newborns.
Temp – Temperature
Body temperature is maintained through the production and loss of heat. This parameter is directly linked to the resistance of the temperature sensor; with the variation of the resistance, the circuit detects and transforms it into a value, whose unit will be expressed in °C or °F, usually.
Multiparameter Monitor Considerations
We can say that, among the thousands of existing electromedical equipment, the multiparameter monitor is on the list of the most important within the hospital. That’s why it is essential that he is always with the maintenance and reports up to date to give the best support to that patient’s life and assistance to the doctor for an accurate diagnosis.


 When Are Dental Implants Necessary?
When Are Dental Implants Necessary?  Arm Day Planning: What You Need to know
Arm Day Planning: What You Need to know  A Clear Understanding CBD and Its Presence in the Human Body
A Clear Understanding CBD and Its Presence in the Human Body  How to Choose the Right Cosmetic Dentist for You In Murray Hills?
How to Choose the Right Cosmetic Dentist for You In Murray Hills?  6 Compelling Benefits of Regular Dental Visits
6 Compelling Benefits of Regular Dental Visits  Dental Braces: Know Before You Get Your Teeth Wired
Dental Braces: Know Before You Get Your Teeth Wired  How platform trolleys and plastic bins optimize your material handling?
How platform trolleys and plastic bins optimize your material handling?  HPC GPUs Take HPC Clusters To The Next Level
HPC GPUs Take HPC Clusters To The Next Level  Unleashing Your Inner Maestro: Why Music Lessons Are More Than Just Learning an Instrument
Unleashing Your Inner Maestro: Why Music Lessons Are More Than Just Learning an Instrument  Blended Families: Including Children in Your Engagement Celebration
Blended Families: Including Children in Your Engagement Celebration